In this article, we’ll dive into some of the most common ADAS systems, the technologies powering them, and the calibration processes necessary to keep them functioning optimally.
1. Lane Departure Warning (LDW):
Lane departure systems are designed to prevent vehicles from drifting out of their lanes unintentionally. Other related systems operating on the same principle include Lane Keep Assist (LKA).
LDW systems typically employ cameras mounted on the front windshield:
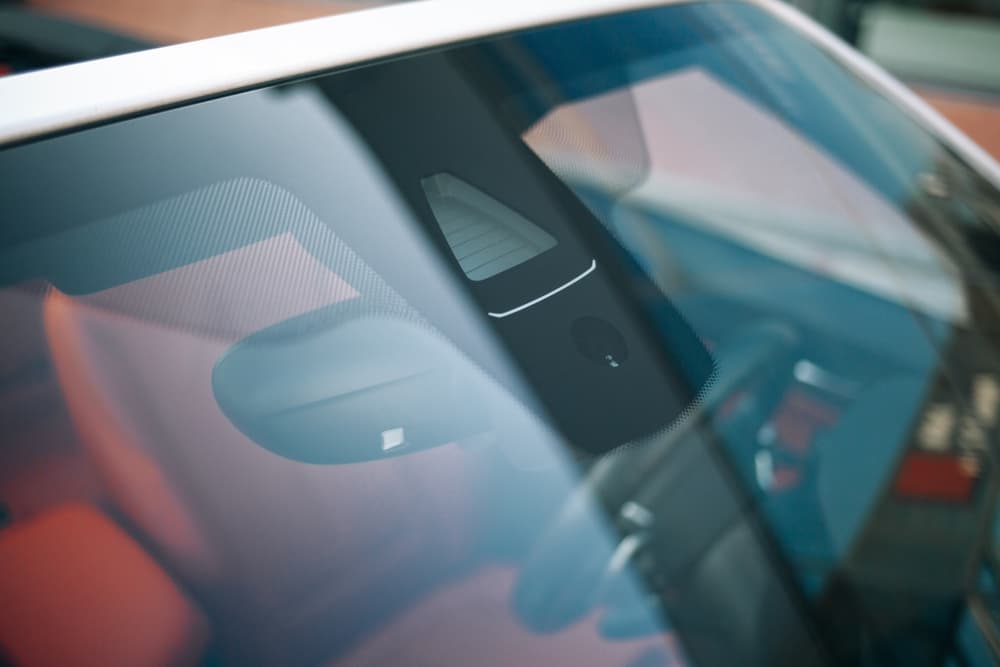

Distinct target patterns are used to calibrate the camera. These are placed on specialized calibration frames such as the IA900 or MA600, ensuring precise alignment according to OEM specifications. The camera on-board the vehicle picks up on these specialized patterns and calibrates its lane-departure warning systems.

2. All View Monitoring (AVM) or Surround View Cameras:
AVM provides drivers with a comprehensive 360-degree view of their surroundings, thanks to strategically placed cameras around the vehicle. Calibration for AVM systems often involves the use of lengthy targets, sometimes exceeding 30 feet, placed on the ground around the vehicle. This calibration process ensures accurate alignment and synchronization of all cameras.

3. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB):
ACC and AEB systems work in tandem to maintain a safe distance from vehicles ahead and automatically apply brakes if a collision is imminent. These systems rely on front radar sensors positioned within the vehicle’s emblem or grille:
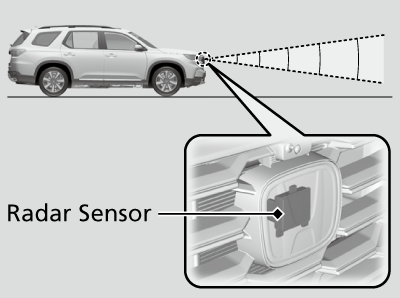
Unlike camera-based systems, radar calibration methods vary and may include the use of doppler radar calibration boxes, metal plates, or reflective mirrors to ensure accurate readings:

4. Rear Collision Warning (RCW) and Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM):
RCW, also known as parking sensors, and BSM utilize small infrared sensors to detect objects in close proximity to the vehicle, alerting the driver to potential hazards:
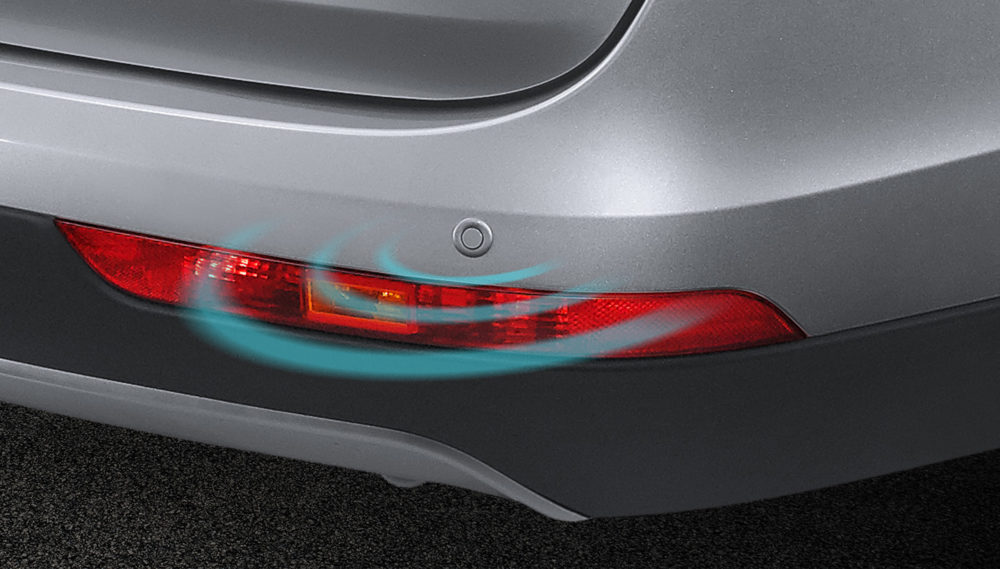

Calibration for these sensors typically involves the use of corner reflectors or PVC pipes to ensure accurate detection and warning capabilities:
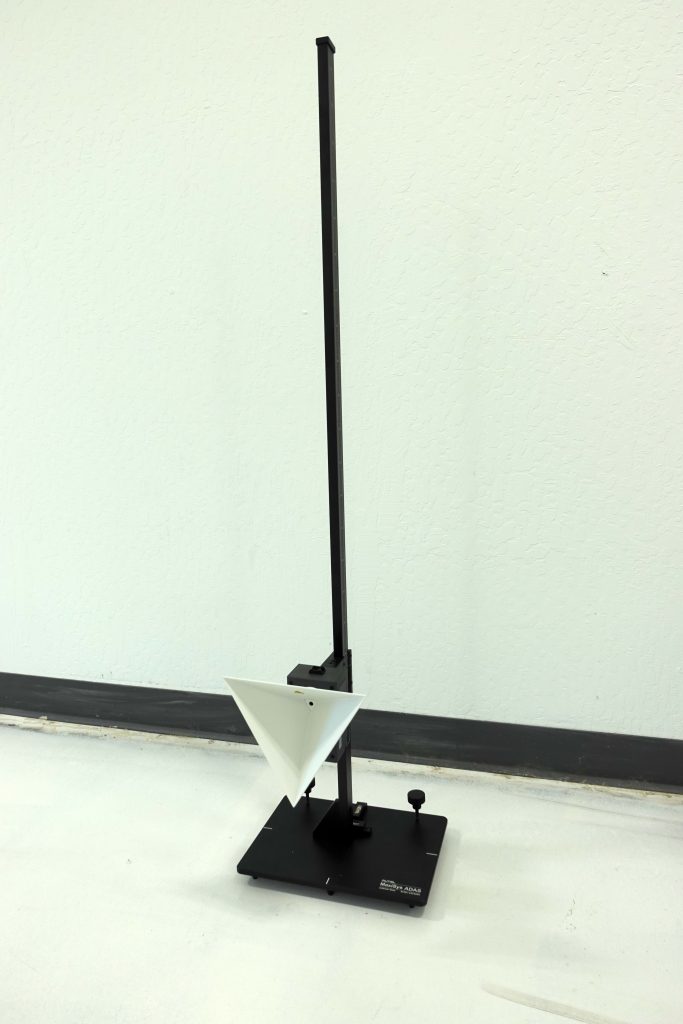
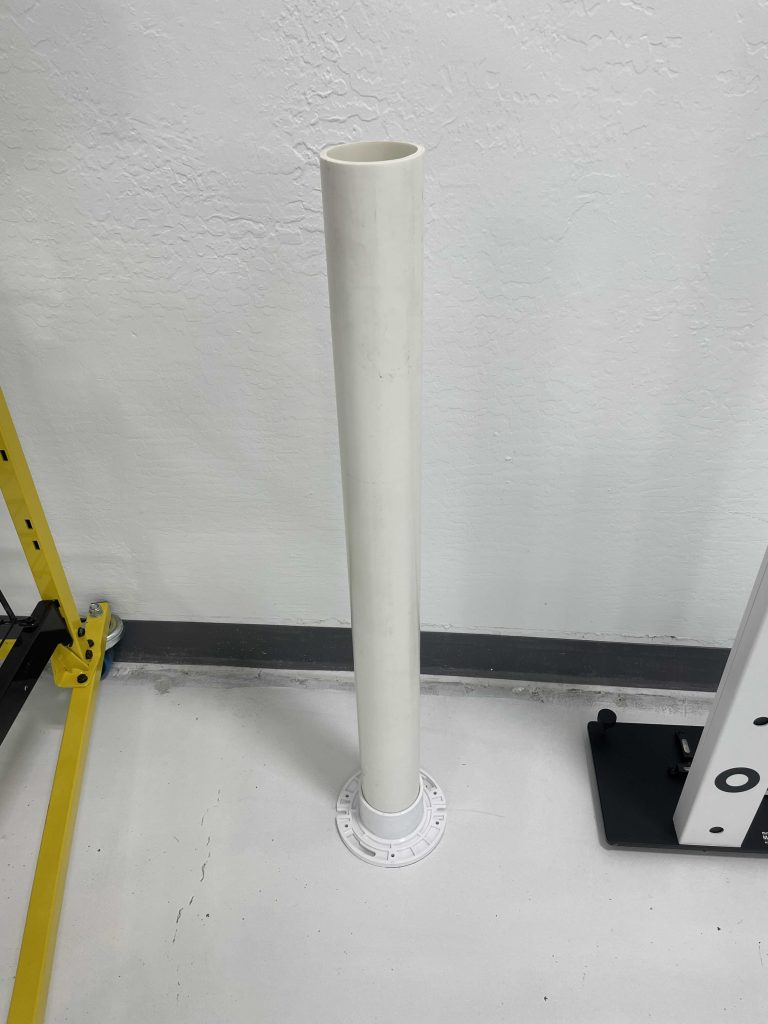


It’s important to note that calibration methods may vary depending on the manufacturer and specific ADAS system. For instance, Honda utilizes cameras for blind spot detection in their LaneWatch system, showcasing the differences in technologies employed across different vehicles.
In conclusion, whether it’s aligning cameras with geometric patterns or fine-tuning radar sensors, proper calibration ensures these systems perform optimally and correctly. As always, please feel free to give us a call at (925) 566-8545 to ask a product specialist any questions you have about ADAS calibrations.
If you liked this content, please subscribe to our newsletter for more great posts.
Leave a Reply