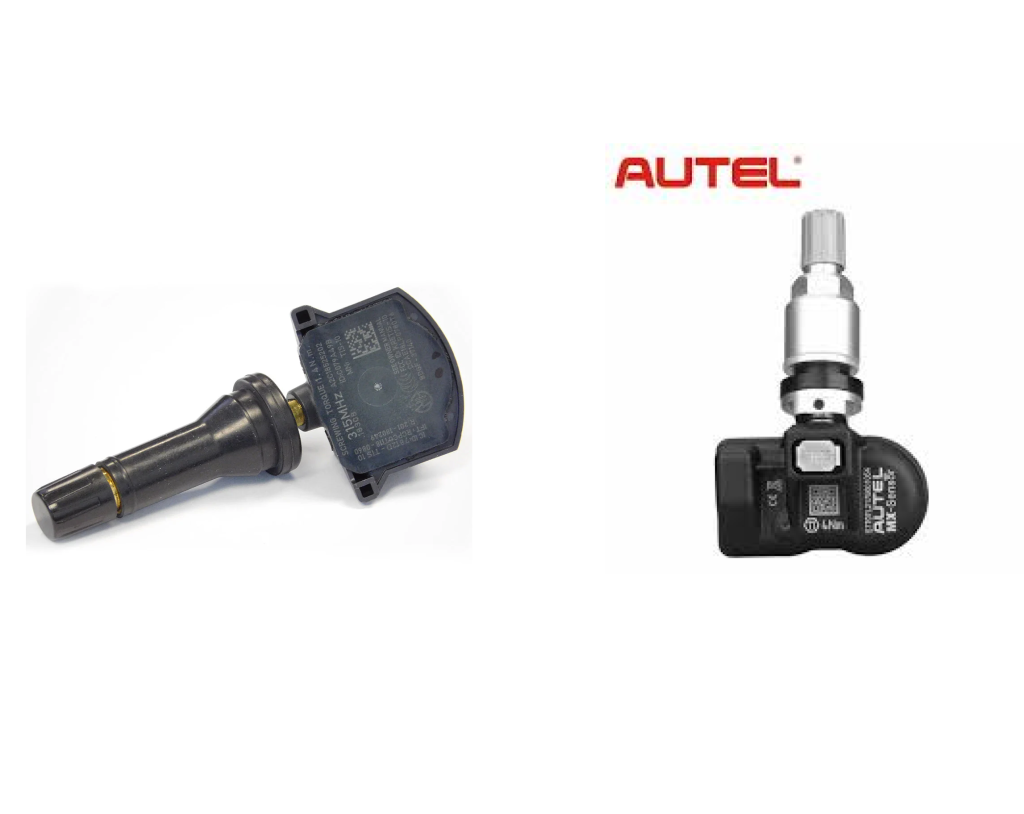

Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) are a growing category within automotive maintenance. Since 2008, all new vehicles have required TPMS. Servicing TPMS is increasingly common amongst not just tire and wheel shops, but also general repair and maintenance shops. When it comes to replacing or upgrading your customers’ TPMS sensors, you have two main options: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) sensors, and aftermarket sensors. Understanding the differences between these two types will help you educate the customer on what best suits their needs and budget.
What Are OEM TPMS Sensors?
OEM TPMS sensors are the sensors that come pre-installed in your vehicle from the manufacturer. They are designed and produced by the same company that made your vehicle, ensuring a perfect fit and compatibility. Here are some key characteristics of OEM TPMS sensors:
- Exact Fit and Compatibility: OEM sensors are specifically designed for your vehicle’s make and model, ensuring a perfect fit and integration with your vehicle’s systems.
- High Quality and Reliability: Since they are made by the vehicle manufacturer, OEM sensors are built to meet strict quality standards. They are perceived to be more reliable and durable than aftermarket options, depending on the aftermarket manufacturer.
- Warranty Coverage: OEM parts typically come with a warranty from the vehicle manufacturer, providing additional peace of mind.
- Higher Cost: The main downside of OEM sensors is their cost. They are generally more expensive than aftermarket sensors, partly due to the brand name and the assurance of quality and compatibility.
What Are Aftermarket TPMS Sensors?
Aftermarket TPMS sensors are produced by third-party manufacturers, such as Autel or Xtool. They are designed to be compatible with a range of vehicle makes and models, but they are not specifically made for any one vehicle. Here are some key characteristics of aftermarket TPMS sensors:
- Cost-Effective: Aftermarket sensors are usually less expensive than OEM sensors, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers. It can run you $100+ dollars for a single OEM sensor; this universal sensor from Autel costs only $29.95.
- Universal: These sensors can be universal across different OEMs. Thus you can buy and stock these sensors without building up too much inventory, which may be the case if you are buying OEM sensors.
- Variable Quality: The quality of aftermarket sensors can vary significantly between manufacturers. Some may offer sensors that are as good as or even better than OEM, while others may fall short in terms of reliability and durability. Rest assured that all the TPMS sensors we sell at ADAS Depot are all of the highest quality.
- Potential Compatibility Issues: Because aftermarket sensors are not made specifically for your vehicle, there may be issues with compatibility. Some sensors may require additional programming or adjustments to work correctly with your vehicle’s TPMS, though most of the major OEMs have good compatibility.
Choosing Between OEM and Aftermarket TPMS Sensors: A Guide for Shop Owners
As a shop owner, selecting the right TPMS sensors for your customers can impact your reputation, customer satisfaction, and bottom line. Here’s a refined look at why you might choose OEM or aftermarket TPMS sensors:
- Budget and Cost-Effectiveness:
- Aftermarket Sensors: These are generally more affordable, making them an attractive option for customers looking to save money. Offering aftermarket sensors can help you cater to budget-conscious clients and increase your sales volume. For customers with older or more common vehicles, aftermarket sensors can provide a cost-effective solution. After around the 5-year mark, we see vehicle owners tend to opt for aftermarket over OEM, but that is by no means a rule
- OEM Sensors: While more expensive, they often justify their higher price with superior quality and reliability. For high-end clients who prioritize performance and are willing to pay a premium, OEM sensors are the preferred choice.
- Inventory:
- Aftermarket Sensors: Since aftermarket sensors cover the majority of all vehicles, you will only have to stock one or a select few types of sensors in your shop.
- OEM Sensors: OEM sensors are pre-programmed, which means you may need to keep an inventory for each OEM.
- Stocking a variety of sensors (both OEM and aftermarket) ensures you can meet diverse customer needs promptly. This flexibility can boost your shop’s reputation for having the right parts in stock.
- Quality and Reliability:
- Aftermarket Sensors: The quality can vary significantly between brands. Partnering with reputable aftermarket manufacturers can provide reliable options that balance cost and quality, but be cautious of lower-quality sensors that might lead to customer dissatisfaction. So only opt for the highest-quality aftermarket sensors, such as Autel or Xtool.
- OEM Sensors: These are manufactured to meet the exact specifications of the vehicle, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal performance. They tend to be more reliable and durable, reducing the likelihood of returns and complaints.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to call us at (925) 566-8545
Leave a Reply